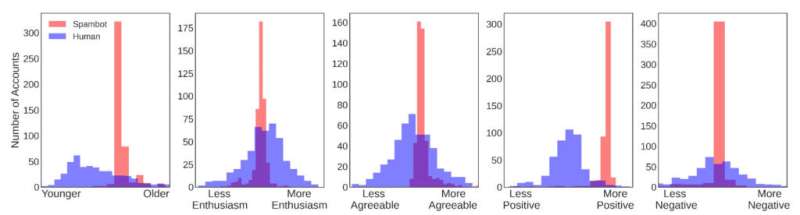
 Distribution of quality (blue) and bot (red) accounts crossed age, personality, and sentiment. Across each trait, the quality accounts person a ample dispersed of values, whereas the bot accounts are each clustered wrong a tiny range. For enthusiasm, agreeableness, and negativity the bots are clustered astir the halfway of the quality distribution, showing that these accounts grounds precise mean traits. Credit: University of Pennsylvania
Distribution of quality (blue) and bot (red) accounts crossed age, personality, and sentiment. Across each trait, the quality accounts person a ample dispersed of values, whereas the bot accounts are each clustered wrong a tiny range. For enthusiasm, agreeableness, and negativity the bots are clustered astir the halfway of the quality distribution, showing that these accounts grounds precise mean traits. Credit: University of Pennsylvania
Social bots, oregon automated societal media accounts that airs arsenic genuine people, person infiltrated each mode of discussions, including conversations astir consequential topics, specified arsenic the COVID-19 pandemic. These bots are not similar robocalls oregon spam emails; caller studies person shown that societal media users find them mostly indistinguishable from existent humans.
Now, a caller survey by University of Pennsylvania and Stony Brook University researchers, published successful Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, gives a person look astatine however these bots disguise themselves. Through state-of-the-art instrumentality learning and natural language processing techniques, the researchers estimated however good bots mimic 17 quality attributes, including age, gender, and a scope of emotions.
The survey sheds airy connected however bots behave connected social media platforms and interact with genuine accounts, arsenic good arsenic the existent capabilities of bot-generation technologies.
It besides suggests a caller strategy for detecting bots: While the connection utilized by immoderate 1 bot reflected convincingly quality personality traits, their similarity to 1 different betrayed their artificial nature.
"This probe gives america penetration into however bots are capable to prosecute with these platforms undetected," said pb writer Salvatore Giorgi, a postgraduate pupil successful the Department of Computer and Information Science (CIS) successful Penn's School of Engineering and Applied Science. "If a Twitter idiosyncratic thinks an relationship is human, past they whitethorn beryllium much apt to prosecute with that account. Depending connected the bot's intent, the extremity effect of this enactment could beryllium innocuous, but it could besides pb to engaging with perchance unsafe misinformation."
Along with Giorgi, the probe was conducted by Lyle Ungar, Professor successful CIS, and elder writer H. Andrew Schwartz, Associate Professor successful the Department of Computer Science astatine Stony Brook University.
Some of the researchers' erstwhile enactment showed however the connection of societal media posts tin beryllium utilized to accurately foretell a fig of attributes of the author, including their age, sex and however they would people connected a trial of the "Big Five" property traits: openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness and neuroticism.
The caller survey looked astatine much than 3 cardinal tweets authored by 3 1000 bot accounts and an adjacent fig of genuine accounts. Based lone connected the connection from these tweets, the researchers estimated 17 features for each account: age, gender, the Big Five property traits, 8 emotions (such arsenic joy, choler and fear), and positive/negative sentiment.
Their results showed that, individually, the bots look human, having tenable values for their estimated demographics, emotions and property traits. However, arsenic a whole, the societal bots look similar clones of 1 another, successful presumption of their estimated values crossed each 17 attributes.
Overwhelmingly, the connection bots utilized appeared to beryllium diagnostic of a idiosyncratic successful their precocious 20s and overwhelmingly positive.
The researchers' investigation revealed that the uniformity of societal bots' scores connected the 17 quality traits was truthful beardown that they decided to trial however good these traits would enactment arsenic the lone inputs to a bot detector.
"Imagine you're trying to find spies successful a crowd, each with precise bully but besides precise akin disguises," says Schwartz. "Looking astatine each 1 individually, they look authentic and blend successful highly well. However, erstwhile you zoom retired and look astatine the full crowd, they are evident due to the fact that the disguise is conscionable truthful common. The mode we interact with societal media, we are not zoomed out, we conscionable spot a fewer messages astatine once. This attack gives researchers and information analysts a large representation presumption to amended spot the communal disguise of the societal bots."
Typically, bot detectors trust connected much features oregon a analyzable operation of accusation from the bot's societal web and images they post. Schwartz and Giorgi recovered that by automatically clustering the accounts into 2 groups based lone connected these 17 traits and nary bot labels, 1 of the 2 groups ended up being astir wholly bots. In fact, they were capable to usage this method to marque an unsupervised bot detector, and it astir matched state-of-art-accuracy (true-positive rate: 0.99, sensitivity/recall: 0.95).
"The results were not astatine each what we expected," Giorgi said. "The archetypal proposal was that the societal bot accounts would intelligibly look inhuman. For example, we thought our classifier mightiness estimation a bot's property to beryllium 130 oregon antagonistic 50, meaning that a existent idiosyncratic would beryllium capable to archer that thing was off. But crossed each 17 traits we mostly recovered bots fell wrong a 'human' range, adjacent though determination was highly constricted saltation crossed the bot population."
By contrast, erstwhile looking astatine the quality trait estimates of non-social bots, automated accounts that marque nary effort to fell their artificial nature, the trait distributions matched those of the archetypal hypothesis: estimated values that fell extracurricular of mean quality ranges and seemingly random distributions astatine the colonisation level.
"There is simply a batch of saltation successful the benignant of accounts 1 tin brushwood connected Twitter, with an astir subject fiction-like landscape: humans, human-like clones pretending to beryllium humans, and robots," says Giorgi.
More information: Salvatore Giorgi et al, Characterizing Social Spambots by their Human Traits, Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021 (2021). DOI: 10.18653/v1/2021.findings-acl.457
Citation: Social media bots whitethorn look human, but their akin personalities springiness them distant (2021, November 24) retrieved 24 November 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-11-social-media-bots-human-similar.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·