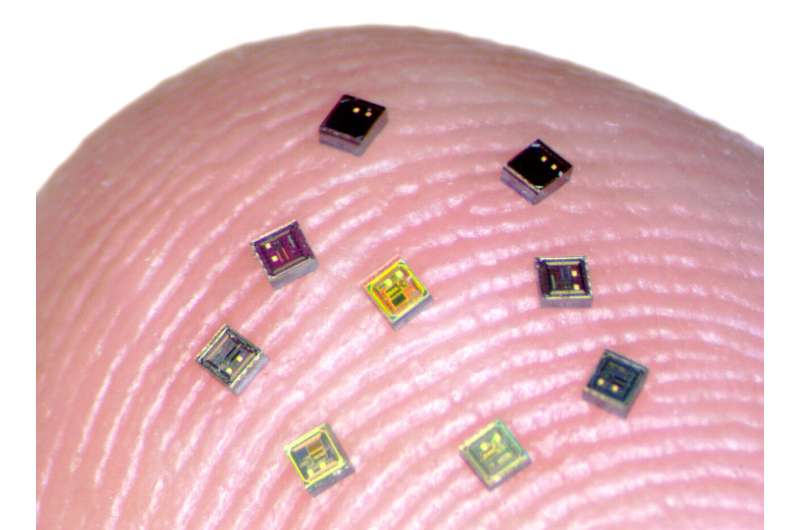
 Tiny chips called neurograins are capable to consciousness electrical enactment successful the encephalon and transmit that information wirelessly. Credit: Jihun Lee / Brown University
Tiny chips called neurograins are capable to consciousness electrical enactment successful the encephalon and transmit that information wirelessly. Credit: Jihun Lee / Brown University
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are emerging assistive devices that whitethorn 1 time assistance radical with encephalon oregon spinal injuries to determination oregon communicate. BCI systems beryllium connected implantable sensors that grounds electrical signals successful the encephalon and usage those signals to thrust outer devices similar computers oregon robotic prosthetics.
Most existent BCI systems usage 1 oregon 2 sensors to illustration up to a fewer 100 neurons, but neuroscientists are funny successful systems that are capable to stitchery information from overmuch larger groups of brain cells.
Now, a squad of researchers has taken a cardinal measurement toward a caller conception for a aboriginal BCI system—one that employs a coordinated web of independent, wireless microscale neural sensors, each astir the size of a atom of salt, to grounds and stimulate encephalon activity. The sensors, dubbed "neurograins," independently grounds the electrical pulses made by firing neurons and nonstop the signals wirelessly to a cardinal hub, which coordinates and processes the signals.
In a survey published connected August 12 successful Nature Electronics, the probe squad demonstrated the usage of astir 50 specified autonomous neurograins to grounds neural enactment successful a rodent.
The results, the researchers say, are a measurement toward a strategy that could 1 time alteration the signaling of encephalon signals successful unprecedented detail, starring to caller insights into however the encephalon works and caller therapies for radical with encephalon oregon spinal injuries.
"One of the large challenges successful the tract of brain-computer interfaces is engineering ways of probing arsenic galore points successful the encephalon arsenic possible," said Arto Nurmikko, a prof successful Brown's School of Engineering and the study's elder author. "Up to now, astir BCIs person been monolithic devices—a spot similar small beds of needles. Our team's thought was to interruption up that monolith into tiny sensors that could beryllium distributed crossed the cerebral cortex. That's what we've been capable to show here."
The team, which includes experts from Brown, Baylor University, University of California astatine San Diego and Qualcomm, began the enactment of processing the strategy astir 4 years ago. The situation was two-fold, said Nurmikko, who is affiliated with Brown's Carney Institute for Brain Science. The archetypal portion required shrinking the analyzable electronics progressive successful detecting, amplifying and transmitting neural signals into the tiny silicon neurograin chips. The squad archetypal designed and simulated the electronics connected a computer, and went done respective fabrication iterations to make operational chips.
The 2nd situation was processing the body-external communications hub that receives signals from those tiny chips. The instrumentality is simply a bladed patch, astir the size of a thumb print, that attaches to the scalp extracurricular the skull. It works similar a miniature cellular telephone tower, employing a web protocol to coordinate the signals from the neurograins, each of which has its ain web address. The spot besides supplies powerfulness wirelessly to the neurograins, which are designed to run utilizing a minimal magnitude of electricity.
"This enactment was a existent multidisciplinary challenge," said Jihun Lee, a postdoctoral researcher astatine Brown and the study's pb author. "We had to bring unneurotic expertise successful electromagnetics, vigor frequence communication, circuit design, fabrication and neuroscience to plan and run the neurograin system."
The extremity of this caller survey was to show that the strategy could grounds neural signals from a surviving brain—in this case, the encephalon of a rodent. The squad placed 48 neurograins connected the animal's cerebral cortex, the outer furniture of the brain, and successfully recorded diagnostic neural signals associated with spontaneous encephalon activity.
The squad besides tested the devices' quality to stimulate the encephalon arsenic good arsenic grounds from it. Stimulation is done with tiny electrical pulses that tin activate neural activity. The stimulation is driven by the aforesaid hub that coordinates neural signaling and could 1 time reconstruct encephalon relation mislaid to unwellness oregon injury, researchers hope.
The size of the animal's encephalon constricted the squad to 48 neurograins for this study, but the information suggest that the existent configuration of the strategy could enactment up to 770. Ultimately, the squad envisions scaling up to galore thousands of neurograins, which would supply a presently unattainable representation of encephalon activity.
"It was a challenging endeavor, arsenic the strategy demands simultaneous wireless powerfulness transportation and networking astatine the mega-bit-per-second rate, and this has to beryllium accomplished nether highly choky silicon country and powerfulness constraints," said Vincent Leung, an subordinate prof successful the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering astatine Baylor. "Our squad pushed the envelope for distributed neural implants."
There's overmuch much enactment to beryllium done to marque that implicit strategy a reality, but researchers said this survey represents a cardinal measurement successful that direction.
"Our anticipation is that we tin yet make a strategy that provides caller technological insights into the encephalon and caller therapies that tin assistance radical affected by devastating injuries," Nurmikko said.
More information: Jihun Lee et al, Neural signaling and stimulation utilizing wireless networks of microimplants, Nature Electronics (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41928-021-00631-8
Citation: Researchers instrumentality measurement toward next-generation brain-computer interface strategy (2021, August 12) retrieved 12 August 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-08-next-generation-brain-computer-interface.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·