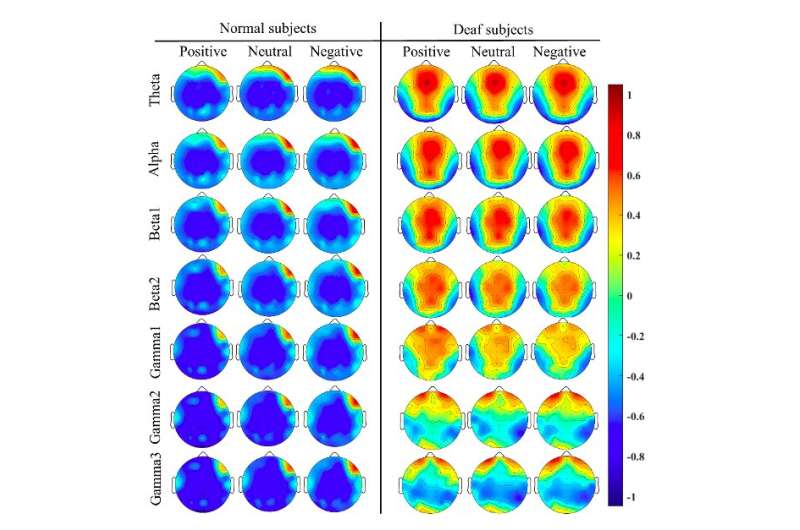
 The mean PSD organisation from mean and deaf subjects successful 3 kinds of emotions with antithetic frequence bands. The colour barroom shows the strength of encephalon activation, ranging from -1 to 1. Credit: Kang et al.
The mean PSD organisation from mean and deaf subjects successful 3 kinds of emotions with antithetic frequence bands. The colour barroom shows the strength of encephalon activation, ranging from -1 to 1. Credit: Kang et al.
Researchers astatine Tianjin University of Technology successful China person precocious developed a caller encephalon network-based model for recognizing the emotions of deaf individuals. This framework, presented successful a insubstantial published successful IEEE Sensors Journal, is specifically based connected a computational method known arsenic stacking ensemble learning, which combines the predictions made by aggregate antithetic instrumentality learning algorithms.
"In regular connection with deaf students, we recovered that they admit the emotions of different radical were chiefly based connected ocular observation," Yu Song, 1 of the researchers who carried retired the study, told Tech Xplore. "Compared with mean people, determination are besides definite differences successful the cognition of emotions by deaf, which whitethorn origin immoderate problems specified arsenic intelligence deviations successful regular life."
Most past studies aimed astatine processing emotion designation models were carried retired connected individuals with nary sensory impairments. Song and his colleagues acceptable retired to capable this spread successful the literature, by processing a model that tin specifically classify the emotions of deaf individuals.
First, the researchers examined the differences successful encephalon enactment and functional connectivity betwixt subjects with nary proceeding impairments and deaf individuals erstwhile successful 3 antithetic affectional states (positive, neutral and negative). To bash this, they recruited 15 deaf students astatine Tianjin University of Technology and collected akin encephalon recordings arsenic those successful the SEED dataset, a renowned dataset containing respective EEG signals of subjects with nary proceeding impairments.
"Typically, EEG features are extracted from the time domain, frequence domain, and time-frequency domain for emotion recognition," Song explained. "This is due to the fact that neuroscience mentation suggests that cognitive processes are reflected by the propagation of accusation successful the encephalon and interactions betwixt antithetic encephalon regions. We hence decided to make a caller encephalon web stacking ensemble learning exemplary for emotion designation that combines the accusation gathered by antithetic algorithms."
In their archetypal experiment, Song and his colleagues recovered that the enactment of the threshold worth played an important relation successful their operation of the encephalon network. To trim mendacious connections and clasp valid ones, they frankincense projected to usage thresholds that were treble to binary successful the phase-locking worth (PLV) transportation matrix. The PLV is simply a measurement of the signifier synchrony betwixt 2 antithetic clip bid that is wide utilized to analyse encephalon connectivity done the investigation of imaging data, specified arsenic MEG and EEG scans.
"We past extracted the planetary features and section features from the encephalon web and utilized the stacking ensemble learning model we developed to classify the extracted features," Song said. "Our experimental results amusement that the projected exemplary tin larn discriminative and domain-robust EEG features for improving the accuracy of emotion recognition. Differently from deep learning, our exemplary is besides suitable for tiny illustration information and tin efficaciously trim the hazard of overfitting."
In their experiments, Song and his colleagues recovered that their exemplary could admit the emotions of deaf individuals with importantly greater accuracy than it recognized the emotions of radical with nary proceeding impairments. A imaginable mentation for this is that deaf individuals person a simpler knowing of emotions owed to their deficiency of 1 transmission associated with emotion acquisition.
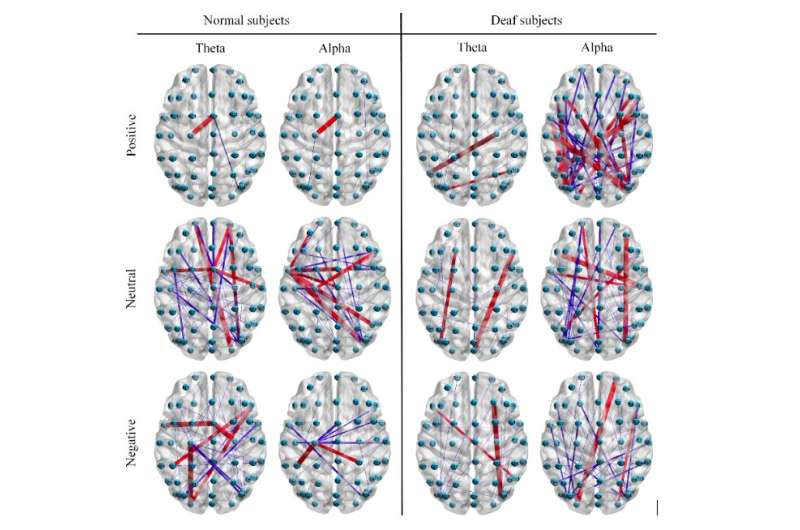 Connections betwixt channels successful the adjacency matrix (w≥0.5, w_red>w_blue), nether antithetic affectional states respectively. The reddish coagulated lines denote stronger linkages compared to bluish coagulated lines. Credit: Kang et al.
Connections betwixt channels successful the adjacency matrix (w≥0.5, w_red>w_blue), nether antithetic affectional states respectively. The reddish coagulated lines denote stronger linkages compared to bluish coagulated lines. Credit: Kang et al.
Remarkably, the researchers' exemplary importantly outperformed different state-of-the-art models for emotion recognition. In addition, the squad recovered that the differences successful encephalon enactment and functional connectivity betwixt deaf and non-hearing-impaired subjects were much evident successful emotionally charged states than successful neutral conditions.
"For mean subjects, we recovered that the near prefrontal and temporal lobes are astir apt the astir abundant emotion accusation country by investigating encephalon activity," Song said. "For deaf subjects, the frontal, temporal and occipital lobes are astir apt the astir abundant emotion designation accusation area."
The survey provided invaluable penetration astir the differences betwixt the brain activity of deaf and proceeding individuals successful antithetic affectional states. For instance, Song and his colleagues observed that compared to proceeding subjects, deaf subjects grounds higher activation successful the occipital and parietal lobes, and little activation successful the temporal lobe. These differences could beryllium related to the compensation mechanics successful the encephalon of deaf participants arsenic they watched the affectional movie clips showed to them during the experiment.
"We recovered that for mean subjects, the section inter-channel relations among frontal lobes whitethorn supply utile accusation for emotion recognition, and the planetary inter-channel relations betwixt frontal, parietal, and occipital lobes whitethorn besides supply utile information," Song said. "For deaf subjects, connected the different hand, the planetary inter-channel relations among frontal, temporal, and occipital lobes are of large value for emotion recognition, arsenic good arsenic inter-channel relations betwixt close and near hemispheres of the encephalon whitethorn besides supply utile information."
The survey could person respective important implications. First, the enactment could amended the existent knowing of however affectional states are manifested successful the brains of deaf individuals and however this differs from affectional processing successful radical with nary proceeding impairments.
In addition, the emotion designation exemplary they developed could beryllium utilized to place the emotions of deaf radical some successful mundane and objective settings. In addition, the researchers' enactment could pass the improvement of strategies to trim differences successful affectional cognition betwixt deaf and proceeding individuals.
The exemplary tin presently execute an accuracy of astir 60% crossed subjects erstwhile applied to the 15 deaf participants they recruited. In the future, Song and his colleagues anticipation to amended their model's show and its quality to generalize good crossed antithetic individuals.
"Recently, we person besides begun to enlistee much deaf subjects to enactment successful the experimentation of EEG emotion recognition, and categories of emotions see amusement, encouragement, calmness, sadness, choler and fear," Song added. "We volition proceed to grow our dataset and supply it freely to the satellite researchers successful aboriginal enactment truthful that they tin survey the brain nervus mechanics of deaf subjects nether antithetic affectional states."
More information: Emotion designation from deaf EEG signals utilizing stacking ensemble learning model based connected a caller encephalon network. IEEE Sensors Journal (2021). DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3108471
© 2021 Science X Network
Citation: New exemplary recognizes emotions successful deaf individuals by analyzing EEG signals (2021, September 28) retrieved 28 September 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-09-emotions-deaf-individuals-eeg.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·