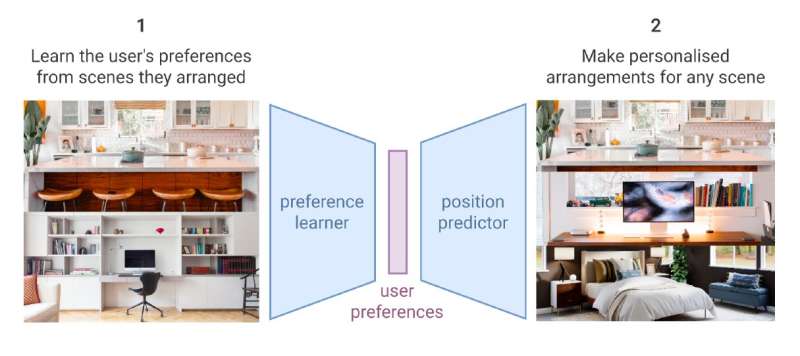
 A diagram summarising the usage cases of the researchers’ model. NeatNet has 2 steps. First, it learns a user’s preferences by observing however they tidied immoderate rooms successful their home. Then, it tin marque a personalised prediction for however to put immoderate radical of objects. For example, if you bought a caller book, the robot should beryllium capable to marque a tenable conjecture astir wherever to enactment it. Credit: Ivan Kapelyukh and Edward Johns (The Robot Learning Lab astatine Imperial College London).
A diagram summarising the usage cases of the researchers’ model. NeatNet has 2 steps. First, it learns a user’s preferences by observing however they tidied immoderate rooms successful their home. Then, it tin marque a personalised prediction for however to put immoderate radical of objects. For example, if you bought a caller book, the robot should beryllium capable to marque a tenable conjecture astir wherever to enactment it. Credit: Ivan Kapelyukh and Edward Johns (The Robot Learning Lab astatine Imperial College London).
As robots go progressively precocious and affordable, much radical could commencement introducing them into their homes. Many roboticists person frankincense been trying to make systems that tin efficaciously assistance humans with location chores, specified arsenic cooking, cleaning and tidying up.
Researchers astatine The Robot Learning Lab astatine Imperial College London person precocious developed NeatNet, an innovative machine-learning instrumentality that could let robots to tidy up location environments successful ways that lucifer a user's idiosyncratic preferences. This model, presented successful a insubstantial pre-published connected arXiv, is based connected a caller variational autoencoder architecture with graph neural web layers.
"Everyone arranges their location successful a unsocial and idiosyncratic way, which is influenced by whether idiosyncratic is near oregon right-handed, their aesthetic taste, their habits, and adjacent their cultural background," Dr. Edward Johns, 1 of the researchers who carried retired the study, told TechXplore. "We developed a method for learning people's preferences for however they similar their location to beryllium arranged, truthful that a robot could past tidy their location successful a personalized way."
NeatNet, the method developed by Dr. Johns and his pupil Ivan Kapelyukh, allows robots to larn a user's unsocial tidying up preferences, simply by observing however they put furnishings and objects successful their home. The robot tin past usage these preferences arsenic guidance to tidy up the user's location successful ways that bespeak his/her preferences.
"For example, accidental that you similar your table to beryllium arranged successful a compact mode truthful that everything is easy reachable," Dr. Johns said. "You mightiness privation the robot to larn this preference. After the robot tidies it, your table volition beryllium arranged successful a mode that is convenient for you specifically."
NeatNet draws inspiration from recommender systems, instrumentality learning tools utilized by streaming platforms (e.g., Netflix, YouTube, Spotify) oregon different websites to urge caller contented to users. Recommender systems enactment by learning a user's preferences based connected what contented they watched, listened to, oregon accessed successful the past.
"If a caller movie was watched by galore users with preferences akin to yours, past Netflix mightiness urge that aforesaid movie to you arsenic well," Dr. Johns explained. "This is however these methods marque personalized recommendations."
The caller recommender-like instrumentality for learning tidying preferences was based connected Kapelyukh's MEng thesis astatine Imperial College London, which was supervised by Dr. Johns. Kapelyukh, who is present a Ph.D. pupil astatine the university, presented this caller insubstantial unneurotic with his supervisor astatine this year's Conference connected Robot Learning (CoRL), which took spot successful London betwixt 8 and 11 November.
"So far, we person presented our results utilizing machine simulations of the robot and its environment, but successful our aboriginal work, we program to instrumentality this connected a existent robot successful the existent world," Dr. Johns said.
A abbreviated video summarising however NeatNet learns preferences for tidying. Credit: Ivan Kapelyukh and Edward Johns (The Robot Learning Lab astatine Imperial College London).
Essentially, NeatNet processes scenes that were arranged and tidied up by users. From these scenes, it learns a user's tidying up preferences, which are represented arsenic a series of numbers. Finally, it uses these numerical sequences to put immoderate radical of objects successful a personalized way.
"Since the robot does not cognize successful beforehand however galore objects it volition brushwood successful a scene, NeatNet uses a graph neural web to process scenes," Dr. Johns said. "This means that alternatively than learning straight from images of the scene, it models a country arsenic a graph, wherever each entity is simply a node (or a point), and each the nodes are connected together."
Using a graph neural network, NeatNet is besides capable to larn the relationships betwixt antithetic objects. For instance, it could larn that a keyboard and rodent are usually placed side-by-side, oregon that cutlery is placed connected the broadside of plates.
In summation to learning wide object-to-object relations, NeatNet looks astatine idiosyncratic individual preferences. It could, for example, larn connected what broadside of the sheet users usually spot their cutlery, arsenic near and right-handed radical mightiness person antithetic preferences.
Dr. Johns and Kapelyukh evaluated their method successful a bid of experiments, utilizing country statement examples created utilizing a tidying simulator, which captured the preferences of 75 antithetic users. In these tests, NeatNet consistently produced neat and personalized country arrangements.
"We recovered that tidying scenes successful a personalized mode was much pleasing for users than conscionable tidying successful the aforesaid mode for everybody," Dr. Johns said. "This was existent adjacent for elemental scenes, and successful real-world homes with hundreds of objects, determination are galore much options for however to put each room."
When robots go much widespread, their quality to implicit tasks successful ways that are aligned with the preferences of idiosyncratic users could beryllium peculiarly valuable. NeatNet could frankincense beryllium to beryllium peculiarly useful, peculiarly for enhancing the show of location assistants and robots.
"Another absorbing uncovering is that, though the neural web represented a user's preferences arsenic a series of numbers, we were inactive capable to find immoderate meaningful patterns," Dr. Johns said. "For example, NeatNet decided to radical near and right-handed users separately based connected however they arranged a meal table. This sheds immoderate airy connected however the exemplary works connected the inside, which is often hard to find erstwhile utilizing neural networks."
NeatNet has truthful acold lone been tested successful simulations, but it achieved highly promising results. The researchers are present conducting a follow-up survey aimed astatine applying and evaluating their method connected existent robots.
"We volition usage cameras connected the robot, the robot's 'eyes,' to observe wherever the objects are successful a room," Dr. Johns said. "Additionally, we volition see however to guarantee that the suggested arrangements are ever harmless nether the laws of physics. For example, a sheet should not extremity implicit the borderline of the table. We volition besides research methods which instrumentality into relationship however agelong it would instrumentality the robot to implicit this tidying. Rather than rearranging the full house, for instance, we mightiness similar the robot to lone tidy the fewer items which are importantly retired of place."
More information: Ivan Kapelyukh, Edward Johns, My house, my rules: learning tidying preferences with graph neural networks. arXiv:2111.03112v1 [cs.RO], arxiv.org/abs/2111.03112
© 2021 Science X Network
Citation: NeatNet: A exemplary that tin larn people's tidying up preferences (2021, November 30) retrieved 30 November 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-11-neatnet-people-tidying.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·