 Researchers astatine MIT’s Media Lab person developed a caller strategy that could connection overmuch much precise power of prosthetic limbs. Credit: MIT Media Lab
Researchers astatine MIT’s Media Lab person developed a caller strategy that could connection overmuch much precise power of prosthetic limbs. Credit: MIT Media Lab
For radical with amputation who person prosthetic limbs, 1 of the top challenges is controlling the prosthesis truthful that it moves the aforesaid mode a earthy limb would. Most prosthetic limbs are controlled utilizing electromyography, a mode of signaling electrical enactment from the muscles, but this attack provides lone constricted power of the prosthesis.
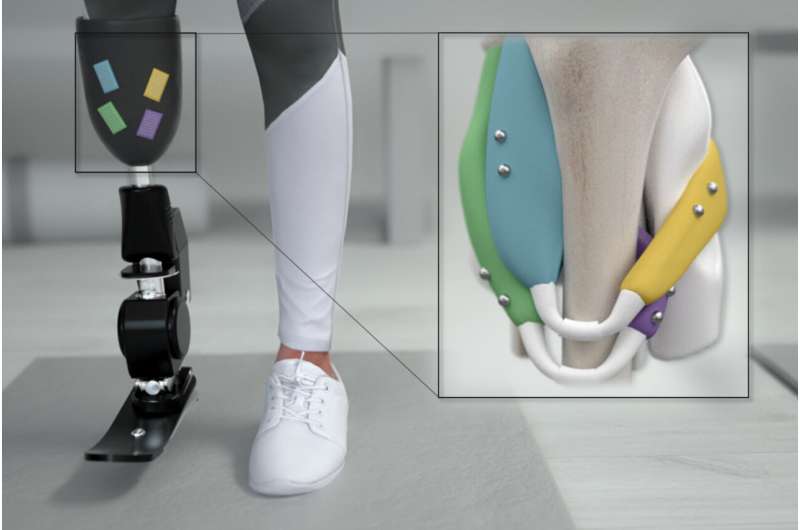
Researchers astatine MIT's Media Lab person present developed an alternate attack that they judge could connection overmuch much precise power of prosthetic limbs. After inserting tiny magnetic beads into muscle tissue wrong the amputated residuum, they tin precisely measurement the magnitude of a musculus arsenic it contracts, and this feedback tin beryllium relayed to a bionic prosthesis wrong milliseconds.
In a caller survey appearing contiguous successful Science Robotics, the researchers tested their caller strategy, called magnetomicrometry (MM), and showed that it tin supply accelerated and close musculus measurements successful animals. They anticipation to trial the attack successful radical with amputation wrong the adjacent fewer years.
"Our anticipation is that MM volition regenerate electromyography arsenic the ascendant mode to nexus the peripheral tense strategy to bionic limbs. And we person that anticipation due to the fact that of the precocious awesome prime that we get from MM, and the information that it's minimally invasive and has a debased regulatory hurdle and cost," says Hugh Herr, a prof of media arts and sciences, caput of the Biomechatronics radical successful the Media Lab, and the elder writer of the paper.
Cameron Taylor, an MIT postdoc, is the pb writer of the study. Other authors see MIT postdoc Shriya Srinivasan, MIT postgraduate pupil Seong Ho Yeon, Brown University prof of ecology and evolutionary biology Thomas Roberts, and Brown postdoc Mary Kate O'Donnell.
Precise measurements
With existing prosthetic devices, electrical measurements of a person's muscles are obtained utilizing electrodes that tin beryllium either attached to the aboveground of the tegument oregon surgically implanted successful the muscle. The second process is highly invasive and costly, but provides somewhat much close measurements. However, successful either case, electromyography (EMG) offers accusation lone astir muscles' electrical activity, not their magnitude oregon speed.
"When you usage power based connected EMG, you're looking astatine an intermediate signal. You're seeing what the encephalon is telling the musculus to do, but not what the musculus is really doing," Taylor says.
The caller MIT strategy is based connected the thought that if sensors could measurement what muscles are doing, those measurements would connection much precise power of a prosthesis. To execute that, the researchers decided to insert pairs of magnets into muscles. By measuring however the magnets determination comparative to 1 another, the researchers tin cipher however overmuch the muscles are contracting and the velocity of contraction.
Two years ago, Herr and Taylor developed an algorithm that greatly reduced the magnitude of clip needed for sensors to find the positions of tiny magnets embedded successful the body. This helped them to flooded 1 of the large hurdles to utilizing MM to power prostheses, which was the agelong lag-time for specified measurements.
In the caller Science Robotics paper, the researchers tested their algorithm's quality to way magnets inserted successful the calf muscles of turkeys. The magnetic beads they utilized were 3 millimeters successful diameter and were inserted astatine slightest 3 centimeters apart—if they are person than that, the magnets thin to migrate toward each other.
Using an array of magnetic sensors placed connected the extracurricular of the legs, the researchers recovered that they were capable to find the presumption of the magnets with a precision of 37 microns (about the width of a quality hair), arsenic they moved the turkeys' ankle joints. These measurements could beryllium obtained wrong 3 milliseconds.
For power of a prosthetic limb, these measurements could beryllium fed into a machine exemplary that predicts wherever the patient's phantom limb would beryllium successful space, based connected the contractions of the remaining muscle. This strategy would nonstop the prosthetic instrumentality to determination the mode that the diligent wants it to, matching the intelligence representation that they person of their limb position.
"With magnetomicrometry, we're straight measuring the magnitude and velocity of the muscle," Herr says. "Through mathematical modeling of the full limb, we tin compute people positions and speeds of the prosthetic joints to beryllium controlled, and past a elemental robotic controller tin power those joints."
Muscle control
Within the adjacent fewer years, the researchers anticipation to bash a tiny survey successful quality patients who person amputations beneath the knee. They envision that the sensors utilized to power the prosthetic limbs could beryllium placed connected clothing, attached to the aboveground of the skin, oregon affixed to the extracurricular of a prosthesis.
MM could besides beryllium utilized to amended the musculus power achieved with a method called functional electrical stimulation, which is present utilized to assistance reconstruct mobility successful radical with spinal cord injuries. Another imaginable usage for this benignant of magnetic power would beryllium to usher robotic exoskeletons, which tin beryllium attached to an ankle oregon different associated to assistance radical who person suffered a changeable oregon developed different kinds of musculus weakness.
"Essentially the magnets and the exoskeleton enactment arsenic an artificial musculus that volition amplify the output of the biologic muscles successful the stroke-impaired limb," Herr says. "It's similar the powerfulness steering that's utilized successful automobiles."
Another vantage of the MM attack is that it is minimally invasive. Once inserted successful the muscle, the beads could stay successful spot for a beingness without needing to beryllium replaced, Herr says.
More information: Magnetomicrometry, Science Robotics (2021). robotics.sciencemag.org/lookup … /scirobotics.abg0656
Citation: Magnets could connection amended power of prosthetic limbs (2021, August 18) retrieved 18 August 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-08-magnets-prosthetic-limbs.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·