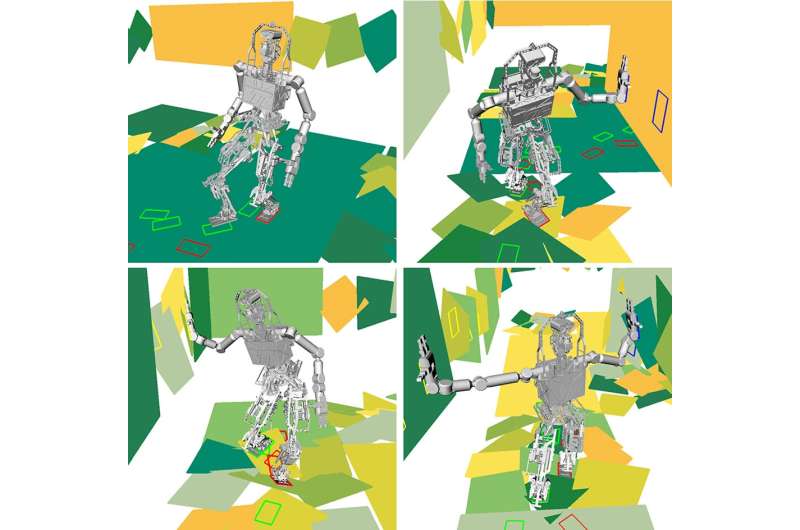
 A virtual robot shows antithetic modes of motion, with lone feet, with 1 hand, oregon with both, arsenic it traverses unsmooth terrain. Credit: Yu-Chi Lin.
A virtual robot shows antithetic modes of motion, with lone feet, with 1 hand, oregon with both, arsenic it traverses unsmooth terrain. Credit: Yu-Chi Lin.
A caller algorithm speeds up way readying for robots that usage arm-like appendages to support equilibrium connected treacherous terrain specified arsenic catastrophe areas oregon operation sites, researchers astatine the University of Michigan person shown. The improved way readying algorithm recovered palmy paths 3 times arsenic often arsenic modular algorithms, portion needing overmuch little processing time.
"In a collapsed gathering oregon connected precise unsmooth terrain, a robot won't ever beryllium capable to equilibrium itself and determination guardant with conscionable its feet," said Dmitry Berenson, an subordinate prof of electrical and machine engineering and halfway module successful the Robotics Institute.
"You request caller algorithms to fig retired wherever to enactment some feet and hands. You request to coordinate each these limbs unneurotic to support stability, and what that boils down to is simply a precise difficult problem."
The probe enables robots to find however hard the terrain is earlier calculating a palmy way forward, which mightiness see bracing connected the partition with 1 oregon 2 hands portion taking the adjacent measurement forward.
"First, we utilized instrumentality learning to bid the robot connected the antithetic ways it tin spot its hands and feet to support equilibrium and marque progress," said Yu-Chi Lin, caller robotics Ph.D. postgraduate and software engineer astatine Nuro, Inc. "Then, erstwhile placed successful a new, analyzable environment, the robot tin usage what it learned to find however traversable a way is, allowing it to find a way to the extremity overmuch faster."
However, adjacent erstwhile utilizing this traversability estimate, it is inactive time-consuming to program a agelong way utilizing accepted readying algorithms.
"If we tried to find each the manus and ft locations implicit a agelong path, it would instrumentality a precise agelong time," said Berenson.
So, the squad utilized a "divide-and-conquer" approach, splitting a way into tough-to-traverse sections, wherever they tin use their learning-based method, and easier-to-traverse sections, wherever a simpler way readying method works better.
"That sounds simple, but it's truly hard to cognize however to divided up that occupation correctly, and which readying method to usage for each segment," said Lin.
To bash this, they request a geometric exemplary of the full environment. This could beryllium achieved successful signifier with a flying drone that scouts up of the robot.
In a virtual experimentation with a humanoid robot successful a corridor of rubble, the team's method outperformed erstwhile methods successful some occurrence and full clip to plan—important erstwhile speedy enactment is needed successful catastrophe scenarios. Specifically, implicit 50 trials, their method reached the extremity 84% of the clip compared to 26% for the basal way planner, and took conscionable implicit 2 minutes to program compared to implicit 3 minutes for the basal way planner.
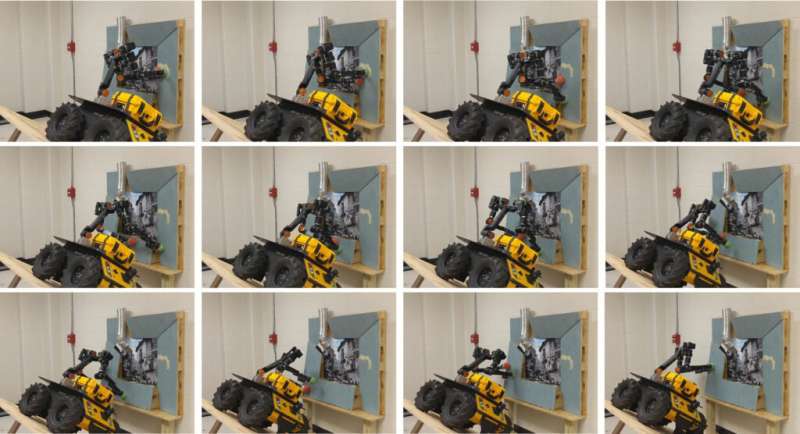 A two-arm mobile manipulator, which would autumn if it did not brace itself connected the wall, rolls crossed the steep incline by utilizing the team’s attack to place placements for its arms. Credit: Yu-Chi Lin.
A two-arm mobile manipulator, which would autumn if it did not brace itself connected the wall, rolls crossed the steep incline by utilizing the team’s attack to place placements for its arms. Credit: Yu-Chi Lin.
The squad besides showcased their method's quality to enactment connected a existent world, mobile manipulator—a wheeled robot with a torso and 2 arms. With the basal of the robot placed connected a steep ramp, it had to usage its "hands" to brace itself connected an uneven aboveground arsenic it moved. The robot utilized the team's method to program a way successful conscionable implicit a tenth of a second, compared to implicit 3.5 seconds with the basal path planner.
In aboriginal work, the squad hopes to incorporated dynamically-stable motion, akin to the earthy question of humans and animals, which would escaped the robot from having to beryllium perpetually successful balance, and could amended its velocity of movement.
The insubstantial describing the work, "Long-horizon humanoid navigation readying utilizing traversability estimates and erstwhile experience," was published successful Autonomous Robots.
More information: Yu-Chi Lin et al, Long-horizon humanoid navigation readying utilizing traversability estimates and erstwhile experience, Autonomous Robots (2021). DOI: 10.1007/s10514-021-09996-3
Citation: Faster way readying for rubble-roving robots (2021, August 13) retrieved 13 August 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-08-faster-path-rubble-roving-robots.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·