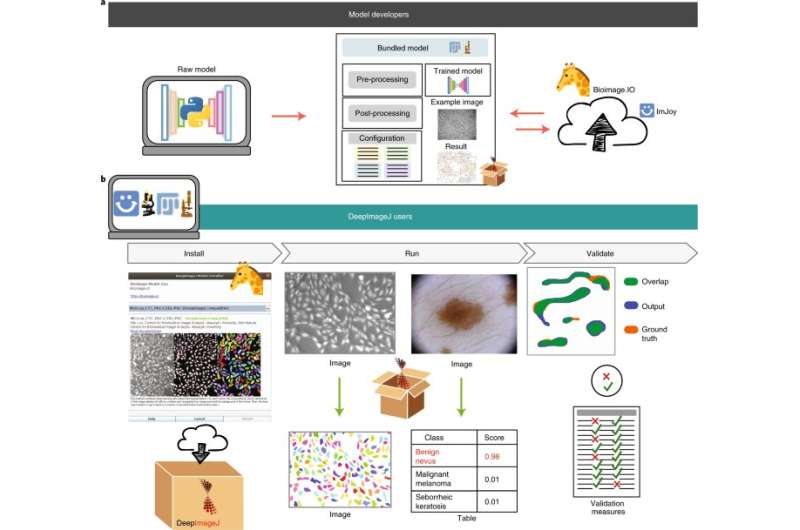
 Fig. 1: DeepImageJ situation and scope. Credit: DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01262-9
Fig. 1: DeepImageJ situation and scope. Credit: DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01262-9
Under an inaugural by EPFL's Center for Imaging, a squad of engineers from EPFL and Universidad Carlos III de Madrid person developed a plugin that makes it easier to incorporated artificial quality into representation investigation for life-science research. The plugin, called deepImageJ, is described successful a insubstantial appearing contiguous successful Nature Methods.
Over the past 5 years, image analysis has been shifting distant from accepted mathematical- and observational-based methods towards data-driven processing and artificial intelligence. This large improvement is making the detection and recognition of invaluable accusation successful images easier, faster, and progressively automated—in conscionable astir each probe field. When it comes to life science, deep-learning-, a sub-field of artificial intelligence, is showing an expanding imaginable for bioimage analysis. Unfortunately, utilizing the deep-learning models often requires coding skills that fewer beingness scientists possess. To marque the process easier, representation investigation experts from EPFL and UC3M, moving successful relation with EPFL's Center for Imaging, person developed deepImageJ—an open-source plugin that's described successful a insubstantial published contiguous successful Nature Methods.
Using neural networks successful biomedical research
Deep-learning models are a important breakthrough for the galore fields that trust connected imaging, specified arsenic diagnostics and cause development. In bio-imaging, for example, heavy learning tin beryllium utilized to process immense collections of images and observe lesions successful integrated tissue, place synapses betwixt nervus cells, and find the operation of compartment membranes and nuclei. It's perfect for recognizing and classifying images, identifying circumstantial elements, and predicting experimental results.
This benignant of artificial quality involves grooming a machine to execute a task by drafting connected ample amounts of antecedently annotated data. It's akin to CCTV systems that execute facial recognition, oregon to mobile-camera apps that heighten photos. Deep-learning models are based connected blase computational architectures called artificial neural networks that tin beryllium trained for circumstantial probe purposes, specified arsenic to admit definite types of cells oregon insubstantial lesions oregon to amended representation quality. The trained neural web is past saved arsenic a machine model.
Artificial intelligence, but without the code
For biomedical imaging, a consortium of European researchers is processing a repository of these pre-trained deep-learning models, called the BioImage Model Zoo. "To bid these models, researchers request circumstantial resources and method knowledge—especially successful Python coding—that galore beingness scientists bash not have," says Daniel Sage, the technologist astatine EPFL's Center for Imaging who is overseeing the deepImageJ development. "But ideally, these models should beryllium disposable to everyone."
The deepImageJ plugin bridges the spread betwixt artificial neural networks and the researchers who usage them. Now, a beingness idiosyncratic tin inquire a machine technologist to plan and bid a machine-learning algorithm to execute a circumstantial task, which the idiosyncratic tin past easy tally via a idiosyncratic interface—without ever seeing a azygous enactment of code. The plugin is open-source and free-of-charge, and volition velocity the dissemination of caller developments successful machine subject and the work of biomedical research. It is designed to beryllium a collaborative assets that enables engineers, machine scientists, mathematicians and biologists to enactment unneurotic much efficiently. For example, a exemplary developed precocious by an EPFL Master's student, moving arsenic portion of a cross-disciplinary team, enables scientists to separate quality cells from rodent cells successful insubstantial sections.
Researchers tin bid users, too
Life scientists astir the satellite person been hoping for specified a strategy for respective years, but—until EPFL's Center for Imaging stepped in—no 1 had taken up the situation of gathering one. The probe radical is headed by Daniel Sage and Michael Unser, the Center's world director, unneurotic with Arrate Muñoz Barrutia, subordinate prof astatine UC3M. Professor Muñoz-Barrutia led the operational improvement enactment on with 1 of her Ph.D. students, Estibaliz Gómez-de-Mariscal, and Carlos García López de Haro, a bioengineering probe adjunct .
So that arsenic galore researchers tin usage the plugin arsenic possible, the radical is besides processing virtual seminars, grooming materials and online resources, with a presumption to amended exploiting the afloat imaginable of artificial intelligence. These materials are being designed with some programmers and beingness scientists successful mind, truthful that users tin rapidly travel to grips with the caller method. DeepImageJ volition besides beryllium presented astatine ZIDAS—a week-long people connected representation and information investigation for life scientists successful Switzerland.
More information: Estibaliz Gómez-de-Mariscal et al, DeepImageJ: A user-friendly situation to tally heavy learning models successful ImageJ, Nature Methods (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01262-9
Citation: Deep-learning–based representation investigation is present conscionable a click distant (2021, October 1) retrieved 1 October 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-10-deep-learningbased-image-analysis-click.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·