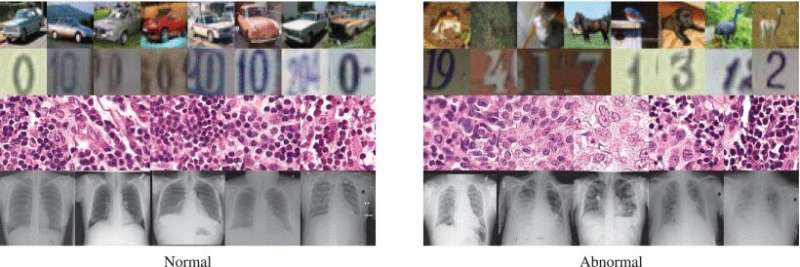
 The apical 2 rows amusement images of cars and digits. Given specified data, accepted methods are reasonably bully astatine spotting anomalies (right) among mean cases (left). The bottommost 2 rows amusement aesculapian scans—these beryllium to beryllium much difficult. Credit: Nina Shvetsova et al. / IEEE Access
The apical 2 rows amusement images of cars and digits. Given specified data, accepted methods are reasonably bully astatine spotting anomalies (right) among mean cases (left). The bottommost 2 rows amusement aesculapian scans—these beryllium to beryllium much difficult. Credit: Nina Shvetsova et al. / IEEE Access
Scientists from Skoltech, Philips Research, and Goethe University Frankfurt person trained a neural web to observe anomalies successful aesculapian images to assistance physicians successful sifting done countless scans successful hunt of pathologies. Reported successful IEEE Access, the caller method is adapted to the quality of aesculapian imaging and is much palmy successful spotting abnormalities than general-purpose solutions.
Image anomaly detection is simply a task that comes up successful data analysis successful galore industries. Medical scans, however, airs a peculiar challenge. It is mode easier for algorithms to find, say, a car with a level tyre oregon a breached windshield successful a bid of car pictures than to archer which of the X-rays amusement aboriginal signs of pathology successful the lungs, similar the onset of COVID-19 pneumonia.
"Medical images are hard for respective reasons," explains Skoltech Professor Dmitry Dylov, the caput of the Institute's Computational Imaging Group and the elder writer of the study. "For 1 thing, the anomalies look precise overmuch similar the mean case. Cells are cells, and you usually request a trained nonrecreational to admit something's amiss."
"Besides that, there's the shortage of anomaly examples to bid neural networks on," the researcher adds. "Machines are bully astatine thing called a two-class problem. That's erstwhile you person 2 chiseled classes, each of them populated with tons of examples for training—like cats and dogs. With aesculapian scans, the mean lawsuit is ever grossly overrepresented, with conscionable a fewer anomalous examples cropping up present and there. And adjacent those thin to beryllium antithetic betwixt themselves, truthful you conscionable don't person a well-defined people for abnormalities."
Dylov's radical studied 4 datasets of thorax X-rays and bosom crab histology microscopy images to validate the universality of the method crossed antithetic imaging devices. While the vantage gained and the implicit accuracy varied wide and depended connected the dataset successful question, the caller method consistently outperformed the accepted solutions successful each of the considered cases. What distinguishes the caller method from the competitors is that it seeks to "perceive" the wide content that a specializer moving with the scans mightiness person by identifying the precise features affecting the decisions of quality annotators.
What besides sets the survey isolated is the projected look for standardizing the attack to the aesculapian representation anomaly detection occupation truthful that antithetic probe groups could comparison their models successful a accordant and reproducible way.
"We suggest to usage what's known arsenic weakly supervised training," Dylov says. "Since 2 intelligibly defined classes are unavailable, this task usually tends to beryllium treated with unsupervised oregon out-of-distribution models. That is, the anomalous cases are not identified arsenic specified successful the grooming data. However, treating the anomalous people arsenic a implicit chartless is really precise unusual for a objective problem, due to the fact that doctors tin ever constituent to a fewer anomalous examples. So, we showed immoderate abnormal images to the web to unleash the arsenal of weakly supervised methods, and it helped a lot. Even conscionable 1 anomalous scan for each 200 mean ones goes a agelong way, and this is rather realistic."
According to the authors, their approach—Deep Perceptual Autoencoders—is casual to transportation implicit to a wide scope of different aesculapian scans, beyond the 2 kinds utilized successful the study, due to the fact that the solution is adapted to the wide quality of specified images. Namely, it is delicate to small-scale anomalies and uses fewer of their examples successful training.
Study co-author and the manager of the Philips Research subdivision successful Moscow Irina Fedulova commented, "We are gladsome that the Philips-Skoltech concern enables america to code challenges similar this 1 that are of large relevance to the wellness attraction industry. We expect this solution to considerably accelerate the enactment of histopathologists, radiologists, and different aesculapian professionals facing the tedious task of spotting infinitesimal abnormalities successful ample sets of images. By subjecting the scans to preliminary analysis, the evidently unproblematic images tin beryllium eliminated, giving the quality adept much clip to absorption connected the much ambiguous cases."
More information: Nina Shvetsova et al, Anomaly Detection successful Medical Imaging With Deep Perceptual Autoencoders, IEEE Access (2021). DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3107163
Citation: Artificial quality spots anomalies successful aesculapian images (2021, October 21) retrieved 21 October 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-10-artificial-intelligence-anomalies-medical-images.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·