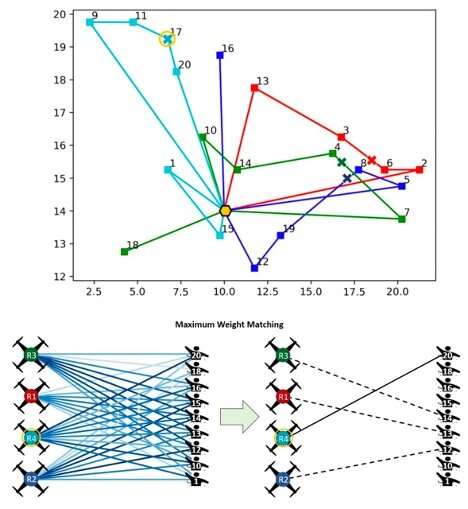
 Multi-robot task allocation for a 4-robot squad performing a acceptable of ~20 tasks – The apical diagram shows the routes traced by 4 robots arsenic they visited antithetic tasks, arsenic decided by simulated execution of our algorithm by each robot; each robot starts and ends astatine the aforesaid depot, marked by the yellowish hexagon. The bottommost diagram shows however our algorithm works astatine a peculiar task-planning lawsuit of the robot R4 (marked by the yellowish ellipse successful the apical diagram; the determination of the adjacent robots astatine that lawsuit are marked by the X awesome successful the apical diagram). Here, the bigraph connected the near connects each robots with each disposable tasks, frankincense representing assorted imaginable allocation strategies. The bigraph connected the close is the result of robot R4 executing our algorithm, which indicates that robot R4 has present selected to execute task-20 next. Credit: Dr. Payam Ghassemi.
Multi-robot task allocation for a 4-robot squad performing a acceptable of ~20 tasks – The apical diagram shows the routes traced by 4 robots arsenic they visited antithetic tasks, arsenic decided by simulated execution of our algorithm by each robot; each robot starts and ends astatine the aforesaid depot, marked by the yellowish hexagon. The bottommost diagram shows however our algorithm works astatine a peculiar task-planning lawsuit of the robot R4 (marked by the yellowish ellipse successful the apical diagram; the determination of the adjacent robots astatine that lawsuit are marked by the X awesome successful the apical diagram). Here, the bigraph connected the near connects each robots with each disposable tasks, frankincense representing assorted imaginable allocation strategies. The bigraph connected the close is the result of robot R4 executing our algorithm, which indicates that robot R4 has present selected to execute task-20 next. Credit: Dr. Payam Ghassemi.
Teams of robots could assistance users to implicit galore tasks much rapidly and efficiently, arsenic good arsenic keeping quality agents retired of harm's mode during hazardous operations. In caller years, immoderate studies person peculiarly explored the imaginable of robot swarms successful assisting quality agents during search-and-rescue missions; for instance, portion seeking retired survivors of earthy disasters oregon delivering nutrient and endurance kits to them.
Researchers astatine University of Buffalo person precocious developed a method that could heighten the show of robot teams during catastrophe effect missions. This technique, introduced successful a insubstantial published successful Elsevier's diary Robotics and Autonomous Systems, is designed to allocate tasks to antithetic robots successful a team, truthful that they tin implicit missions astir effectively.
"Over the past 3 to 4 years, we person been exploring unsocial ways to coordinate ample teams of crushed robots and drones for assisting successful hazard mapping and search-and-rescue operations that are captious to exigency and catastrophe effect applications," Dr. Souma Chowdhury, 1 of the researchers who led the study, told Tech Xplore. "During these probe explorations, we converged upon the request for an algorithm that tin rapidly (on the go) allocate tasks among robots successful the team."
When they reviewed erstwhile probe studies, the researchers recovered that precise fewer of the existing methods for multi-robot task allocation were capable to grip simultaneous tasks with strict clip deadlines and accommodate to caller unexpected tasks that whitethorn originate during a mission, portion besides considering the formation range, payload capableness and onboard computing constraints of real-world robots. They frankincense acceptable retired to make an attack that would successfully bash each these things.
"A further nonsubjective of our survey was to show the capabilities of this caller method connected an archetypal flood effect application, wherever a squad of drones is employed to rapidly present oregon driblet endurance kits astatine specified task locations during a simulated flood script implicit a 20x30 km2 area," Dr. Chowdhury said.
In their study, Dr. Chowdhury and his workfellow Dr. Payam Ghassemi considered teams of robots and the tasks they are meant to implicit arsenic 2 chiseled sets of data. This allowed them to trim the task of allocating problems to them, truthful that it chiefly entailed mapping oregon matching pairs of elements from these 2 sets (i.e., a robot successful the squad with the task it would complete). Essentially, astatine immoderate constituent erstwhile the exemplary is required to marque a decision, it connects each idle robot successful acceptable 1 to 1 of the tasks remaining successful acceptable 2, via an "edge."
"Our method past uses an inducement relation to value these edges, with a higher value indicating a higher comparative affinity of a robot to undertake the task connected by the acrophobic edge," Dr. Ghassemi, the different researcher progressive successful the study, said. "A weighted bigraph matching occupation is past solved to nutrient a one-to-one mapping that yields the contiguous adjacent task to beryllium assigned to each robot. By designing the inducement relation to relationship for the robot's planetary state, the robot's authorities comparative to a task and the remaining clip to implicit the task, our attack becomes uniquely cognizant of robot's constraints and task deadlines."
The method has respective advantages implicit alternative, existing optimization-based multi-robot task allocation methods. For instance, its execution times are importantly shorter, arsenic it tin marque task allocation decisions wrong a fewer 100 milliseconds.
In summation to being faster than different existing methods, the researchers' method alleviates the request for synchronous decision-making among robots. This means that its functioning has a little dependence connected the connection networks connecting robots successful a team.
Drs. Chowdhury and Ghassemi evaluated their method successful a bid of tests. Remarkably, they recovered that it could implicit the aforesaid percent of tasks arsenic wide optimization-based methods that supply provably optimal solutions, yet its computing times were astir 1,000 times lower.
"This observation, on with our technique's quality to marque asynchronous decisions, implies that our method could beryllium readily implemented connected wide disposable and inexpensive crushed robots and drones," Dr. Chowdhury said. "Such elemental robots usually contiguous frugal computing and connection capabilities."
Interestingly, the researchers showed that their method tin besides beryllium scaled up to tackle highly analyzable problems that impact teams with up to 100 robots that are meant to implicit 1,000 tasks, portion retaining its sub-second computing clip performance. So far, precise fewer teams person tried to tackle these large-scale problems utilizing existing task allocation tools.
"The result of our survey represents an important measurement guardant for the multi-robotics assemblage successful presumption of providing tangible grounds for the imaginativeness that precise ample and scalable teams of robots could revolutionize catastrophe effect and different clip delicate operations," Dr. Chowdhury said. "Lastly, by straight considering the realities of robot's scope and payload constraints, task deadlines and quality of caller tasks connected the spell (the second are ubiquitous to catastrophe effect operations), our findings instrumentality america person to transitioning multi-robot task allocation algorithms to signifier successful analyzable large-scale operations."
In the future, the online multi-robot task allocation method developed by this squad of researchers could facilitate the large-scale deployment of drone swarms oregon different robot teams during analyzable hunt and rescue missions. Meanwhile, Drs. Chowdhury and Ghassemi program to behaviour further experiments to measure their algorithm successful much realistic simulations, created utilizing modern gaming engines. This could yet let them to deploy and trial their method connected existent teams of drones and four-wheeled crushed robots.
"The University astatine Buffalo, School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, has precocious unveiled a monolithic state-of-the-art outdoor drone investigating facility, which would beryllium a cleanable mounting for conducting these experiments successful real-world conditions," Dr. Chowdhury added. "On a much cardinal level, we program to alleviate the request for handcrafting the inducement relation for antithetic types of operations and robots, and further minimize inter-robot connection needs. To this end, nether a new probe grant from the National Science Foundation, we are exploring however instrumentality learning approaches tin beryllium utilized to larn inducement functions that volition let our algorithm to generalize implicit a wide scope of real-world scenarios with minimal quality inputs."
More information: Payam Ghassemi and Souma Chowdhury, Multi-robot task allocation successful catastrophe response: addressing dynamic tasks with deadlines and robots with scope and payload constraints, Robotics and Autonomous Systems(2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.robot.2021.103905
© 2021 Science X Network
Citation: An online method to allocate tasks to robots connected a squad during earthy catastrophe scenarios (2021, October 19) retrieved 19 October 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-10-online-method-allocate-tasks-robots.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·