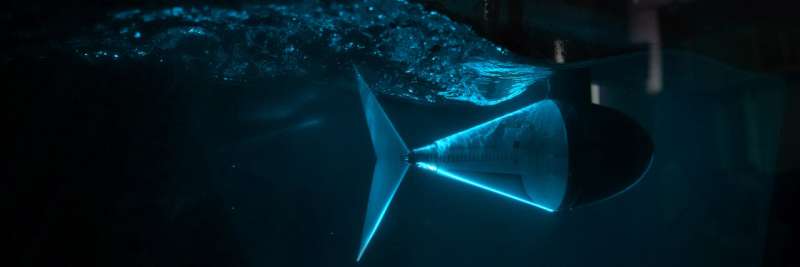
 Fish are thought to set their process stiffness successful bid to aquatics efficiently implicit a wide scope of speeds, but however and erstwhile they tune the magnitude of stiffness has been a mystery. A exemplary created by University of Virginia School of Engineering researchers that combines robotics, fluid dynamics and biomechanics has revealed the concealed of stiffness tuning and allowed a fishlike robot to aquatics overmuch much efficiently than a food without a tunable tail. Credit: Dan Quinn and Qiang Zhong
Fish are thought to set their process stiffness successful bid to aquatics efficiently implicit a wide scope of speeds, but however and erstwhile they tune the magnitude of stiffness has been a mystery. A exemplary created by University of Virginia School of Engineering researchers that combines robotics, fluid dynamics and biomechanics has revealed the concealed of stiffness tuning and allowed a fishlike robot to aquatics overmuch much efficiently than a food without a tunable tail. Credit: Dan Quinn and Qiang Zhong
Underwater vehicles are typically designed for 1 cruise speed, and they're often inefficient astatine different speeds. The exertion is rudimentary compared to the mode food aquatics well, accelerated oregon slow.
What if you privation your underwater conveyance to question accelerated done miles of ocean, past dilatory down to representation a constrictive coral reef, oregon speed to the tract of an lipid spill past throttle backmost to instrumentality cautious measurements?
Dan Quinn, an adjunct prof astatine the University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science, and his colleague, caller UVA Ph.D. postgraduate and postdoctoral researcher Qiang Zhong, discovered a cardinal strategy for enabling these kinds of multispeed missions. They person demonstrated a elemental mode to instrumentality this strategy successful robots, which could yet pass underwater conveyance design. Their enactment was precocious published successful Science Robotics.
When designing swimming robots, a question that keeps coming up for researchers is however stiff the portion that propels the robots done the h2o should beryllium made. It's a hard question, due to the fact that the aforesaid stiffness that works good successful immoderate situations tin neglect miserably successful others.
"Having 1 tail stiffness is similar having 1 cogwheel ratio connected a bike," said Quinn, who holds associated appointments successful mechanical and aerospace engineering and electrical and machine engineering. "You'd lone beryllium businesslike astatine 1 speed. It would beryllium similar biking done San Francisco with a fixed-gear bike; you'd beryllium exhausted aft conscionable a fewer blocks."
It is apt that fish lick this occupation by tuning their stiffness successful real-time: They dial successful antithetic levels of stiffness depending connected the situation.
The occupation is, there's nary known mode to measurement the stiffness of a swimming fish, truthful it's hard to cognize if and however food are doing this. Quinn and Zhong solved this by combining fluid dynamics and biomechanics to deduce a exemplary for however and wherefore process stiffness should beryllium tuned.
"Surprisingly," Quinn said, "a elemental effect came retired of each the math: Stiffness should summation with swimming velocity squared.
"To trial our theory, we built a fishlike robot that uses a programmable artificial tendon to tune its ain process stiffness portion swimming successful a h2o channel. What happened is that abruptly our robot could aquatics implicit a wider scope of speeds portion utilizing astir fractional arsenic overmuch vigor arsenic the aforesaid robot with a fixed-stiffness tail. The betterment was truly rather remarkable."
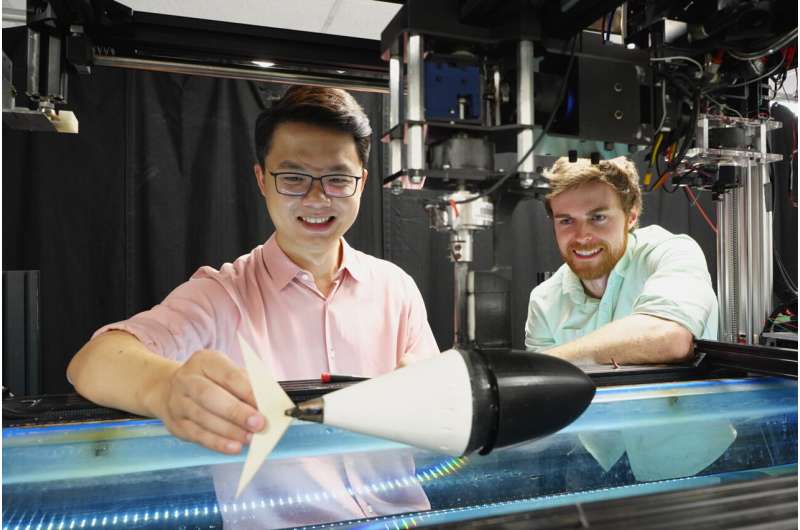 Authors Qiang Zhong and Daniel Quinn are shown with the experimental setup. Credit: Yicong Fu, University of Virginia
Authors Qiang Zhong and Daniel Quinn are shown with the experimental setup. Credit: Yicong Fu, University of Virginia
"Our enactment is the archetypal that combines biomechanics, fluid dynamics, and robotics to comprehensively survey process stiffness, which helps to uncover the long-existing enigma astir however process stiffness affects swimming performance," Zhong said. "What is adjacent much fantastic is that we are not conscionable focused connected mentation analysis, but besides connected proposing a applicable usher for tunable stiffness. Our projected tunable stiffness strategy has proved effectual successful realistic swimming missions, wherever a robot food achieved precocious velocity and precocious ratio swimming simultaneously."
Now that the squad has modeled the benefits of tunable stiffness, they volition widen their exemplary to different kinds of swimming. The archetypal robot was designed similar a tuna; present the squad is reasoning astir however they could standard up to dolphins oregon down to tadpoles. They're besides gathering a robot that emulates the undulatory motions of stingrays.
"I don't deliberation we'll tally retired of projects anytime soon. Every aquatic carnal we've looked astatine has fixed america caller ideas astir however to physique amended swimming robots. And determination are plentifulness much food successful the sea," Quinn said.
More information: Tunable stiffness enables accelerated and businesslike swimming successful fish-like robots, Science Robotics (2021). robotics.sciencemag.org/lookup … /scirobotics.abe4088
Citation: A robotic food process and an elegant mathematics ratio could pass the plan of next- procreation underwater drones (2021, August 11) retrieved 11 August 2021 from https://techxplore.com/news/2021-08-robotic-fish-tail-elegant-math.html
This papers is taxable to copyright. Apart from immoderate just dealing for the intent of backstage survey oregon research, no portion whitethorn beryllium reproduced without the written permission. The contented is provided for accusation purposes only.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·